Suppose you’re a website owner or a digital marketer. You probably know how important it is to index your website pages by Google or any search engine.
It’s the first step towards getting your website to appear in Google search results. But how do you know if your website has been indexed? That’s where a Google index checker tool helps you and comes in handy.
This blog post will show you how to build a SERP API index checker tool for indexing web pages quickly & reliably. Here, we only talk about the Google platform for other search engines. The process & methods are the same as Google.
Before going further, we must know what SERP API is & why it is needed to make a high-performance tool.
SERP API allows access to search engine results page data programmatically. To get reliable & fast access to SERP data from search engines without losing your precious time.
Try SERPHouse APIs to automate many SEO tasks, allowing developers to get access smoothly to build tools, market research, and many more.
Read more: How Digital Marketer Can Get Benefit from SERP APIs?
SERPHouse mainly works on these Search engines to retrieve data.
- Bing
- Yahoo
Why use Google Index Checking API to Build an Index Checker Tool?
The best option for building an index checker tool is using Google index checker API because it provides accurate and up-to-date data.
Google changes its algorithm frequently, and if you use a tool that scrapes Google search results, you may need more accurate or updated data.
API also provides data in a structured format, which makes it easy to process and analyze.
Getting Started with SERP API from SERPHouse.com
To start with SERPHouse, sign up for an account on our website. We offer a free plan that allows you to make up to 100 monthly requests.
If you need more recommendations, you can upgrade to a paid plan.
Once you’ve signed up, you’ll receive an API key that you can use to access their API.
You can find the documentation on our website explaining how to use API.
Building the Google Index Checker Tool
To build a Google indexing checker tool, you must request Google to check if your website appears in the search results. Here’s the code snippet to do that:
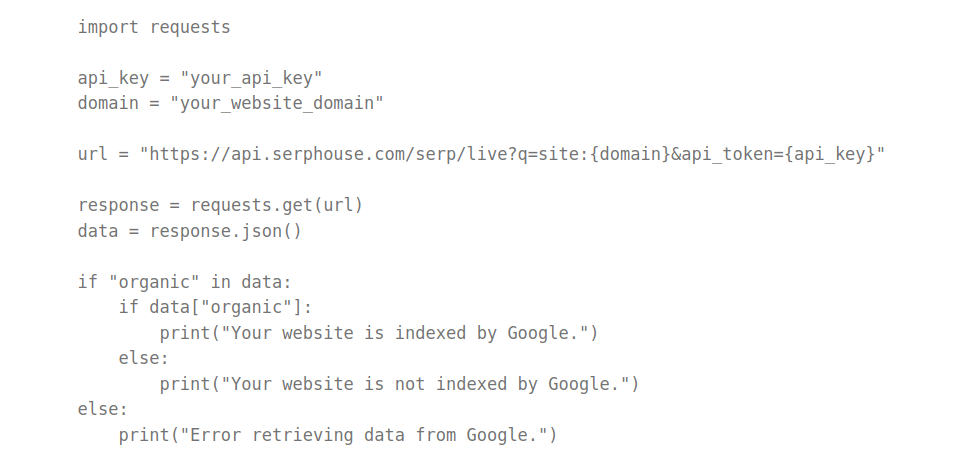
Let’s break down the code.
First, import the requests library, which allows us to make HTTP requests. Then, we set the api_token variable to our API key from SERPHouse.com and the domain variable to our website’s domain name.
Next, we construct the URL to request SERP API. We use the site operator to search for our website in Google’s index. And use api_token in the URL to authenticate a request.
Then, make the request using the requests.get() method and store the response in the response variable. We then parse the JSON data using the response.json() method and store it in the data variable.
Finally, we check if the “organic” key exists, and it is not empty. Then, print a message saying that Google indexes the website.
If it’s open, publish a statement saying that Google does not index the website. We print an error message if the “organic” key doesn’t exist.
Thanks for Reading.

