Table of Contents
Table of Contents
As developers, we constantly interface with APIs, whether to integrate third-party services, get data, or automate processes. However, one important issue that we often ignore or misinterpret is API rate limits. It is something that can determine the success of an integration or service.
If you’ve ever had a perfectly fine API connection suddenly stop working, you’ve probably hit a rate limit. In this post, we’ll dig into the world of API rate limits: what they are, why they exist, how they affect developers, and—most importantly—how to work around them so your apps keep humming.
What Are API Rate Limits?

Simply put, API rate limiting is a constraint that restricts the number of API requests a user (or program) can send over a given time. Imagine you are trying to interact with an API that acts like a proxy for some service. The service wants to ensure that no one user or app overwhelms its servers with excessive queries.
Each API also has rules on the number of queries made within a specified time, which can be minutes, hours, or days. In this case, the API returns an error when the number of allowable queries is exceeded, stating that you have reached the rate limit.
Think of it as a toll booth: each request you make is like paying a toll, but after a certain number of tolls (requests) you are told to wait until the next time starts.
Why Do APIs Have Rate Limits?
You might wonder why APIs enforce rate limits in the first place. There are several good reasons for this:
- Prevent Overloading Servers: The most common reason for rate limits is to prevent the API’s infrastructure from overloading with requests, especially during high-traffic periods.
- Ensure Fair Usage: Without rate limiting, one user could consume all of the API’s resources, leaving little for others. This enables equal access to the API for everyone.
- Manage Resources: Many APIs are paid services, and rate limitations allow the API provider to manage the cost of the service by limiting users to a finite number of queries.
- Security and Abuse Prevention: Rate limiting can help prevent abuse, such as brute-force attacks or bots attempting to flood the server.
Common Types of Rate Limiting
API rate limiting isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Different APIs use different strategies for limiting the number of requests. Here are the most common types:
1. Fixed Window Limiting: This is the most straightforward method of rate limiting. It limits the number of requests that can be made in a given time (for example, 100 per hour). Once that limit has been reached, the user must wait until the next window starts.
2. Sliding Window Limiting: This one is more exciting. Instead of a fixed time window, the limit is applied to the most recent set number of requests over a rolling period. For example, you can submit 100 requests within the last 60 minutes. As time passes, older requests “fall off,” making a place for new ones.
3. Leaky Bucket Algorithm: Think of this as a bucket with a small hole in it. The rate of requests represents the flow of water into the bucket. If requests arrive too quickly, the bucket overflows and the requests are denied. However, the requests drain at a consistent rate, allowing for increases in traffic while limiting the total number of requests over time.
4. Token Bucket Algorithm: In this method, tokens are added to a bucket at regular intervals. To submit a request, a token is consumed. If there are no available tokens, the request will be rejected. This system supports burst traffic as long as tokens are available, but it limits the rate at which requests can be made over time.
How Can Rate Limiting Affect Your Application?
As a developer, hitting an API rate limit can be frustrating, especially if your application is dependent on a steady stream of requests. Here’s how rate limiting can impact you:
- Interrupted Service: If you exceed the rate limit, your API calls will fail, disrupting the service you’re providing.
- Error Responses: When the rate limit is exceeded, most APIs provide HTTP status codes like 429 Too Many Requests. These responses suggest that limitations have been reached, but do not offer immediate solutions.
- Increased Latency: If you utilise an API with strict rate limits, you may see longer wait times between queries, which may slow down your app’s performance.
How to Handle API Rate Limits?
Now that we’ve covered how rate limits work and why they exist, let’s look at how to deal with them successfully.
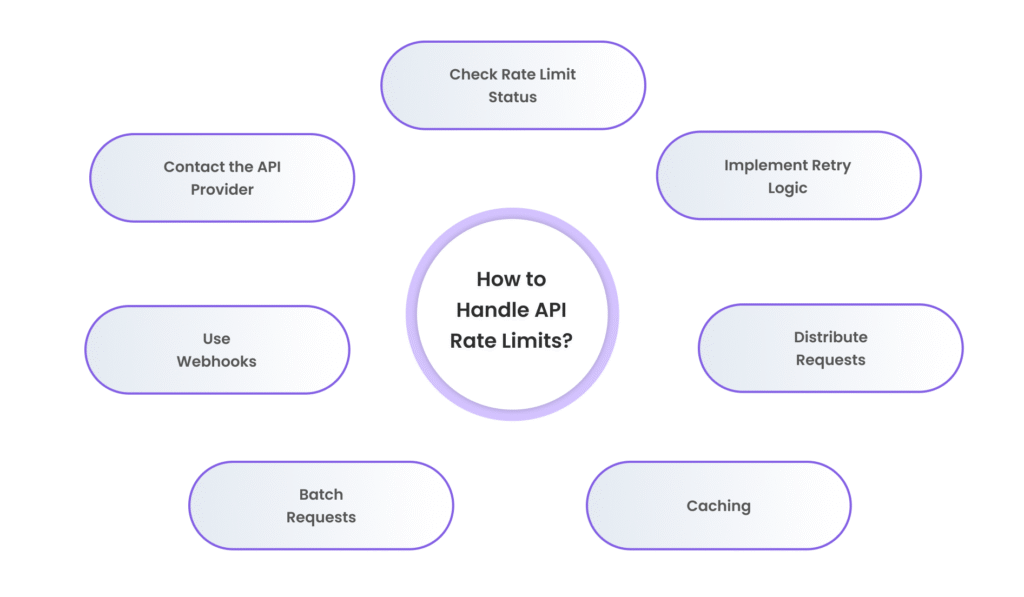
1. Check Rate Limit Status: Many APIs include endpoints where you can check your current status for your rate limit. For example, a service like GitHub features an X-RateLimit-Remaining header indicating how many more requests are left in that rate limit.
2. Implement Retry Logic: When the app hits the rate limit, it is vital to back off and try again after some time. Implementing automatic retry with exponential backoff ensures that your application can handle the rate limits efficiently.
3. Distribute Requests: If you have many services, you can also distribute the requests across different API keys, accounts, or endpoints to reduce the effects of rate limiting.
4. Caching: This can be beneficial for data that is requested frequently. This will also reduce the frequency of API requests made by your app since it can serve data from the cache instead of re-accessing it.
5. Batch Requests: Some APIs allow you to gather many queries into a single one, which reduces the total number of requests. If this is a possibility, it can be an effective way to control rate limits while still obtaining the data you need.
6. Use Webhooks: If available, webhooks could be an excellent alternative to making frequent API queries. Instead of continuously searching for fresh data, webhooks allow the API to notify you of changes.
7. Contact the API Provider: If your application requires higher limits, many API providers will let you request them, either through a subscription plan or by negotiating a higher quota.
Best Practices for Managing API Rate Limits
Here are a few best practices to keep in mind when dealing with API rate limits:
- Understand the Rate Limiting Policy: Always check the API documentation to understand the rate restriction policy before interacting with it. This will help you understand the regulations and how to apply them.
- Use Efficient Algorithms: Optimize your application’s logic to avoid needless API requests. Avoid sending many requests for the same data that hasn’t changed.
- Monitor Your Usage: Set up monitoring to track how close you are to your rate limits, and make sure your app handles this gracefully before you reach the threshold.
Conclusion
API rate limitations are required to provide both developers and API providers fairness, security, and stability. Understanding and planning how it works will help you avoid service outages and ensure your apps run smoothly.
Implementing solutions such as retry logic, caching, and request dispersion can help you work around rate limits and keep your applications running smoothly. Always be aware of the API’s limitations and take proactive measures to restrict your usage.
If you’ve reached an API rate limit, don’t panic. With the appropriate technique and foresight, your app will manage rate limits like a pro.